When it comes to assessing an unresponsive victim, understanding the components of a pulse is crucial. As a first responder or someone trained in basic life support, being able to accurately assess the presence or absence of a pulse can determine the next steps in providing life-saving interventions.
The pulse serves as a vital indicator of the victim’s cardiovascular function, providing valuable information about their overall health and well-being. By assessing the pulse, one can gather important data on the rate, rhythm, and quality of the victim’s heartbeat.
These components can offer insights into potential underlying medical conditions or the severity of the situation at hand. In this article, I will delve into each component of a pulse, explaining what they mean and how they can guide your actions in providing immediate care.
What Are the Components of a Pulse Check in an Unresponsive Victim
When assessing the pulse of an unresponsive victim, it is essential to understand the components that make up this vital sign. By examining these components, healthcare professionals can gather crucial information about the victim’s cardiovascular function and overall health.
Rate
The rate of a pulse refers to the number of beats per minute (BPM). In an unresponsive victim, a normal resting heart rate typically ranges from 60 to 100 BPM. However, it is important to note that certain factors, such as age and physical condition, can influence the baseline heart rate. A significantly high or low pulse rate may indicate a medical condition or the severity of the situation.
Rhythm
The rhythm of a pulse refers to the regularity of the beats. A normal pulse should have a steady, regular rhythm. However, an irregular pulse rhythm may suggest an underlying cardiovascular issue, such as atrial fibrillation. In an unresponsive victim, an irregular pulse rhythm should be further evaluated to determine the appropriate course of action.
Quality
The quality of a pulse refers to the strength and volume of each beat. In an unresponsive victim, a strong and regular pulse indicates good cardiovascular function. Conversely, a weak or absent pulse may indicate poor circulation or cardiac arrest. Assessing the quality of the pulse can help healthcare professionals determine if immediate life-saving interventions, such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), are necessary.
Understanding the components of a pulse in an unresponsive victim is crucial for accurate assessment and appropriate intervention. By evaluating the rate, rhythm, and quality of the pulse, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into the victim’s condition and make informed decisions regarding their care.
Importance of Checking a Pulse
Ensuring Proper Blood Flow
Checking a pulse in an unresponsive victim is a critical step in assessing their overall health and determining the need for immediate intervention. By understanding the components of a pulse, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information about the victim’s cardiovascular function.
One of the primary reasons for checking a pulse is to ensure proper blood flow throughout the body. The pulse rate, which refers to the number of beats per minute, gives insight into the efficiency of the heart in pumping blood. A rapid pulse rate may indicate a potential problem, such as an irregular heartbeat or inadequate oxygen supply to the body’s tissues. On the other hand, a slow pulse rate may suggest a decrease in cardiac output or an underlying medical condition. By assessing the pulse rate, healthcare professionals can evaluate the adequacy of blood flow and promptly address any abnormalities.
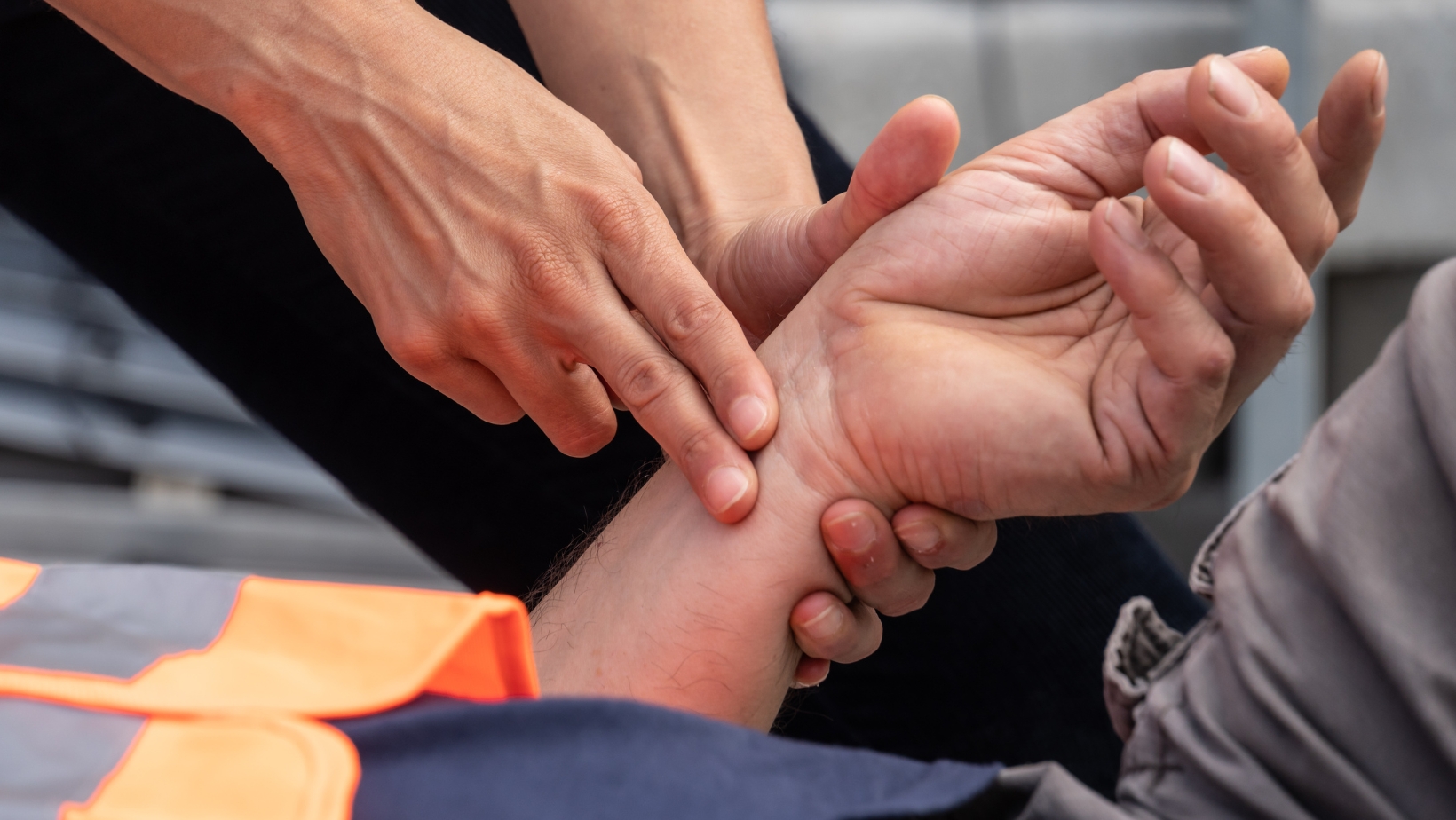
Assessing Cardiac Function
Another crucial aspect of checking a pulse is to assess the victim’s cardiac function. The rhythm of the pulse, which refers to the regularity of the beats, provides valuable information about the heart’s electrical activity. A regular rhythm indicates a normal heartbeat, while an irregular rhythm may suggest arrhythmias or other cardiac disorders. Identifying an irregular pulse rhythm is essential as it may require immediate medical attention to prevent further complications.
In addition to the rhythm, the quality of the pulse is also assessed. The quality refers to the strength and volume of each beat. A strong and bounding pulse may indicate normal cardiac function, while a weak or thready pulse may suggest inadequate blood flow or a decrease in cardiac output. Evaluating the pulse quality can help healthcare professionals determine if the victim’s heart is effectively pumping blood to meet the body’s needs.
By understanding the components of a pulse check in an unresponsive victim, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information about their cardiovascular function. Assessing the pulse rate, rhythm, and quality enables prompt identification of any abnormalities, allowing for timely interventions and potentially saving lives.